When discussing web automation, we have particularities that make it more powerful and efficient in some contexts. Parallel execution with Python code increases efficiency by executing multiple tasks simultaneously. When dealing with large-scale challenges, this approach significantly reduces overall processing time.
As an implementation example, we can execute several automations in parallel when we use web drivers.
How does the webdriver work?
The webdriver provides a connection protocol with browsers, allowing you to control them with a set of interfaces that allow you to discover and manipulate the Document Object Model (DOM).

This communication occurs via the HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) protocol. The webdriver provides a list of endpoints that receive commands and generate actions (such as clicks) or return information (such as text) from a specific page or element.
When we find a button element, we can click on it. The webdriver performs this click action through an API call, freeing up the computer’s resources.
It is possible to perform parallel execution of web automation precisely because of this characteristic; the calls are individual and linked to a webdriver session, meaning there is no interference between the executions of different automation, not even allocation of I/O (input/output) resources on the machine.
Python code example + webdriver
To illustrate the construction of web automation, we will use the BotCity project template to carry out a simple process:
- Open the browser on the Google page;
- Search by search box’s DOM element;
- Enter the text;
- Search for the DOM element of the ‘I’m feeling lucky’ button;
- Click on the ‘I’m feeling lucky’ button;
- Wait for the page to load completely;
- Each time the page is loaded, a different image appears;
- Take a screenshot;
- Send the screenshot to the BotCity Orchestrator;
- Finish the task.
Identify the bot.py file and change it as follows:
# Imports from the BotCity framework and BotCity Orchestrator SDK from botcity.web import WebBot, Browser, By from botcity.maestro import * # Disables errors if not connected to Orchestrator BotMaestroSDK.RAISE_NOT_CONNECTED = False def main(): # BotMaestroSDK instance for integration with Orchestrator maestro = BotMaestroSDK.from_sys_args() execution = maestro.get_execution() print(f"Task ID is: {execution.task_id}") print(f"Task Parameters are: {execution.parameters}") # WebBot instance bot = WebBot() # Configures the browser to run in headless mode bot.headless = True # Select the browser that you want to use bot.browser = Browser.FIREFOX # Sets the webdriver path bot.driver_path = "resources\geckodriver.exe" # Open your browser and navigate to the Google website bot.browse("https://www.google.com") # Find textbox DOM element text_box = bot.find_element("APjFqb", By.ID) # Enter text in the text box text_box.send_keys("This person does not exist") # Find 'I'm Feeling Lucky' button DOM element lucky_botton = bot.find_element( ".FPdoLc > center:nth-child(1) > input:nth-child(2)", By.CSS_SELECTOR ) # Click the button lucky_botton.click() # Wait 3 seconds until the page is loaded bot.wait(3000) # Take a screenshot bot.save_screenshot(r"resources\screenshot.png") # Send the screenshot to the Orchestrator maestro.post_artifact( task_id=execution.task_id, artifact_name="screenshot.png", filepath=r"resources\screenshot.png" ) # Close the browser bot.stop_browser() # Completing the task in the Orchestrator maestro.finish_task( task_id=execution.task_id, status=AutomationTaskFinishStatus.SUCCESS, message="Task completed successfully!" ) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
How to manage parallel executions?
To run parallel task execution, the best option is to use an automation orchestration tool, such as BotCity Orchestrator. To do this, we need the following requirements:
- Web automation that interacts with browsers via webdrivers;
- Separate Runners to execute multiple tasks in parallel (each Runner executes one task at a time).
Furthermore, we can still parallelize these executions with desktop-type automation, which uses I/O resources and computer vision to perform tasks.
Web automation can be configured to run in “headless mode” without loading the graphical interface, acting as a service on the machine.
This way, while web automation runs unseen, we leave resources free for computer vision to operate in the same environment.
Step by step for orchestration
For this example, we will run a desktop automation that uses the environment’s resources, computer vision, and keyboard inputs. At the same time, we will run web automation in parallel, in headless mode, without the need for a graphical interface, thus not interfering with the desktop automation.
Step 1:
Create the Runners in BotCity Orchestrator. Configure them with the “background” type to run web automation and the “desktop” type to run desktop automation. Also, follow the runner setup step by step in the documentation.

Step 2:
Choose the environment where all the automations will run and install it via the BotCity SDK wizard.
Após a instalação, precisamos garantir que os runners serão identificados corretamente.
Então dentro da pasta de cada um, identifique o arquivo conf.bcf na pasta conf.
Dentro deste arquivo, ajuste o machineID com os nomes dos runners criados.
Dessa forma cada Runner poderá executar uma tarefa diferente.

Step 3:
Create and deploy automations on the platform.

Step 4:
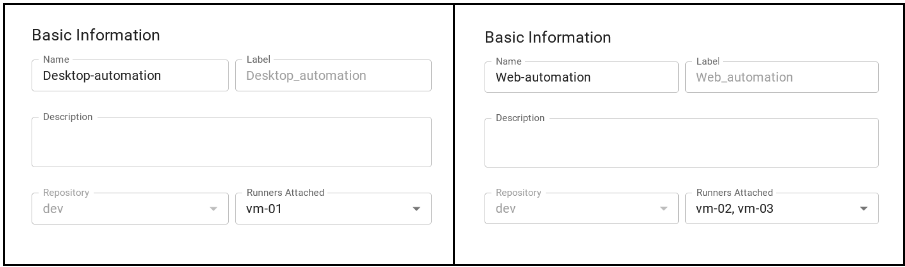
Link each automation to the runners created earlier. Note that the desktop automation was linked to the “vm-01” runner only, while the web automation was related to the “vm-02” and “vm-03” runners.
Step 5:
Create multiple tasks to run in parallel.

Step 6:
When you click “start” on the runners’ interface, they will connect to the BotCity Orchestrator, accessing the task queue and searching for those linked to their machineID. This way, each Runner can execute a different task in the queue.
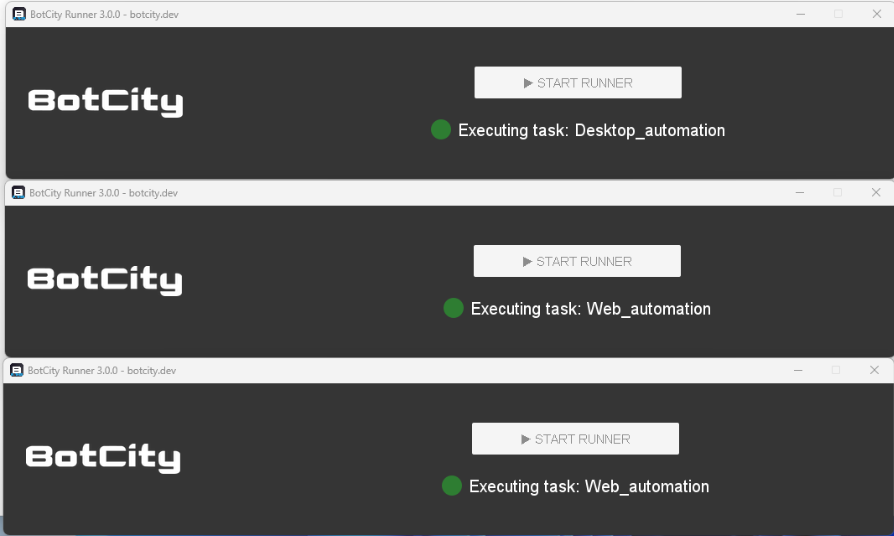
Result
After the execution is finished, the photos captured in the process will be available for download in the result files menu.


In this context, the more Runners available, the more tasks you can execute in parallel. Remembering that the environment must also support the execution of these tasks for efficient execution, always check the configurations of the running computer or virtual machine to decide the ideal number of Runners.
Have multiple parallel automations with Python RPA
If you are looking for a Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solution to create and orchestrate automation in Python, we recommend you check out BotCity, which has a Python code assistant and a Python automation orchestrator for complex operations. You can create a free account and test the entire process we present here. If you have any questions, feel free to send them to forum.