In today’s era of hyperautomation, the rise of hybrid automation models and multi-vendor RPA architectures—combining low-code automation with Python-based automation—has made security a critical concern. Particularly with programming languages like Python, where flexibility comes with significant responsibilities in orchestration and governance.
For CoE leaders and RPA developers, securing Python-based RPA automation is essential to protect sensitive data, maintain control over environments and processes, and ensure operational governance. Security should never be an afterthought—any vulnerabilities can lead to severe financial and reputational damage.
In this guide, we’ll explore key security pillars in Python RPA and best practices for governance. Want to dive deeper? Take our free course on Python RPA Security.
Key Security Pillars in Python RPA
To safeguard Python-based automation—widely adopted for its versatility and AI compatibility—organizations must ensure their automations are not only efficient but also resilient and reliable. Some key security pillars in Python RPA include:
- Access control for sensitive data
- Isolation of robot execution environments
- Log management, error handling, and alerting
- Role-based access control and permissions
- Credential management
- Centralized and protected credential storage
- Audit and monitoring mechanisms
Now, let’s take a deep dive into the best practices automation teams should implement when orchestrating Python-based RPA workflows.
Read more: Why Python RPA Integrations Are More Secure Than Low-Code Connectors?
1. Access Control for Data in RPA
When automating business processes involving confidential data, it’s crucial to execute automations within your own infrastructure, ensuring full control over where and how data and documents are processed. Consider the following aspects:
Security Policies
Review your company’s security policies to understand restrictions on different types of documents. Ensure that processing occurs internally and aligns with security regulations.
Temporary File Deletion
During automation execution, temporary files are often created to facilitate data manipulation. It’s essential to delete these files once the automation is completed to prevent unauthorized access.
Data Access Segregation
As automation initiatives scale, more people may become involved, increasing the need for controlled access to information.
Implement role-based access controls by department, team, or user group to ensure individuals only have access to the data necessary for their tasks. This maintains data integrity and prevents unauthorized access.
2. Isolation of Execution Environments in RPA
Network segmentation is a crucial isolation measure. IT teams should configure segmentation so that RPA execution environments have restricted access only to the necessary network resources. Below are some best practices:
Access Control for Virtual Machines (VMs)
Enforce strict access policies for VMs, containers, and other execution environments. In some cases, systems may remain logged in continuously, posing a significant security risk. Robust access management and monitoring are essential.
Session Control
During automation execution, ensure that only necessary sessions are active within operating systems. Implement mechanisms to dynamically create and terminate sessions based on automation needs, maximizing security and efficiency.
3. Log Management, Error Handling, and Alerts
Whether automating vendor approval in ERP systems, financial reconciliation, or document generation, maintaining detailed execution logs is crucial.
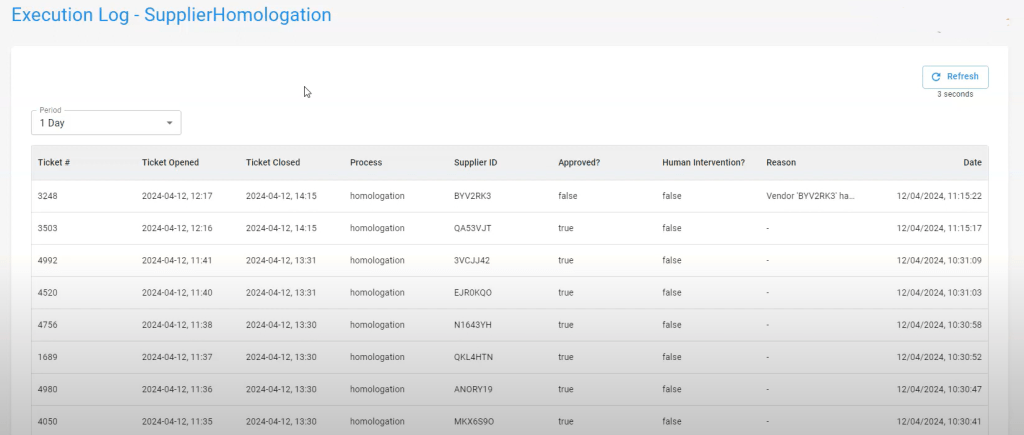
Execution Logs in Python RPA
By leveraging logging tools and RPA orchestration platforms, teams can monitor each step of the automation process in real-time.
For example, BotCity Orchestrator allows developers to send execution logs using a simple Python command, ensuring seamless integration and operational transparency. See an example below:
 Log management is handled directly within the orchestrator’s dashboard.
Log management is handled directly within the orchestrator’s dashboard.
Learn more: https://blog.botcity.dev/2024/03/14/logs-in-python-for-rpa-automation-example/
Error Management in Python RPA
In RPA development, errors are more common than in other types of software development, often due to automation and system updates or poorly formatted user inputs.
The orchestration platform plays a crucial role in monitoring these errors and notifying the team for quick intervention and necessary adjustments.
This can be easily managed using the platform’s API, such as BotCity, which allows error commands to be sent for better visibility and handling within the orchestrator.
 If you’re already using BotCity and want to monitor errors, access the error module to view details such as the automation ID, error message, automation version, programming language used, and other relevant data.
If you’re already using BotCity and want to monitor errors, access the error module to view details such as the automation ID, error message, automation version, programming language used, and other relevant data.
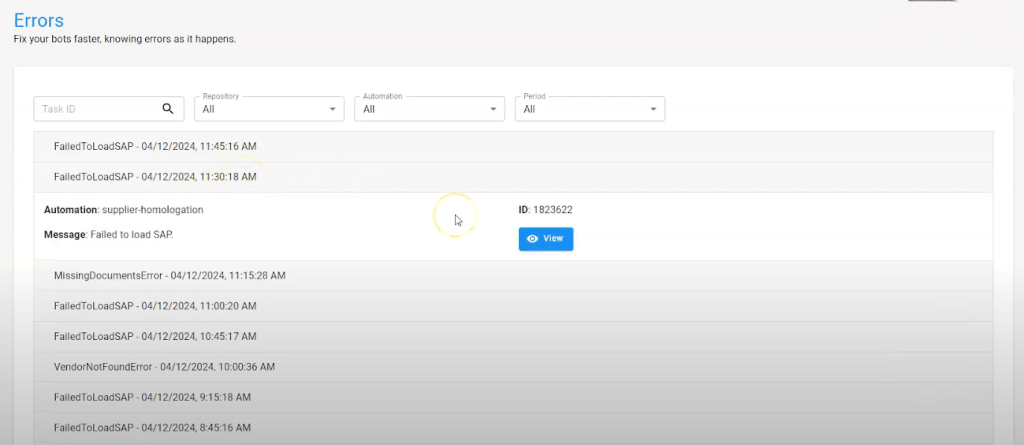 The stack trace shows the exact line where the error occurred, a screenshot at the moment of the error, and tags related to the execution context, along with attached files that help troubleshoot the issue.
The stack trace shows the exact line where the error occurred, a screenshot at the moment of the error, and tags related to the execution context, along with attached files that help troubleshoot the issue.
 Know more: https://blog.botcity.dev/2024/03/28/rpa-errors-management/
Know more: https://blog.botcity.dev/2024/03/28/rpa-errors-management/
Alerts for Technical and Business Users
During automation execution, it may be necessary to notify the team about important events for various reasons. In BotCity, the Alerts Module simplifies this communication. Alerts can be configured to appear in the web interface or be sent via API to emails, WhatsApp, and other communication channels.
From a development perspective, implementing alerts in BotCity Orchestrator is straightforward: the developer simply needs to insert a Python command to trigger the alert, specifying the alert type and message.
 You can then view the list of alerts, including the automation that triggered the alert, task ID, message, and the repository to which the automation belongs.
You can then view the list of alerts, including the automation that triggered the alert, task ID, message, and the repository to which the automation belongs.

4. Access Control and Permissions for Python Orchestration
For security reasons, it is recommended to organize users into groups, such as teams or departments, to ensure controlled access to the information and resources necessary for their roles. This enhances productivity, governance, and security.
In orchestration platforms like BotCity, for example, three roles define access and permissions:
- Developers: Can manage automation development and deployment.
- Operators: Can use and monitor automations, typically business users.
- Administrators: Have full supervision and audit capabilities, ideal for CoE and automation leaders.
Creating User Groups and Automation Repositories
Regardless of the platform you use, it is essential to create user groups and repositories to segment automations and manage access for specific departments and users.
In BotCity Orchestrator, creating a group is simple—just define a name, label, and description. By leveraging repositories to segregate information, you can specify which user groups have access to certain data and resources, improving security and organization.

Credential Management
For security reasons, credentials should never be embedded directly in automation source code, especially considering the potential impact of credential updates on production automations.
To address these challenges, we recommend using a credential management module, which can be implemented in different ways depending on your company’s security policies. Here are some alternatives:
Password Vaults
For companies that prefer to keep credentials in-house, local password vaults can securely store credentials within the company’s own infrastructure.
Cloud-Based Credential Management
Solutions like AWS Secrets Manager and HashiCorp Vault offer secure cloud-based credential management. BotCity provides plugins that simplify integration with these platforms, ensuring secure credential handling.
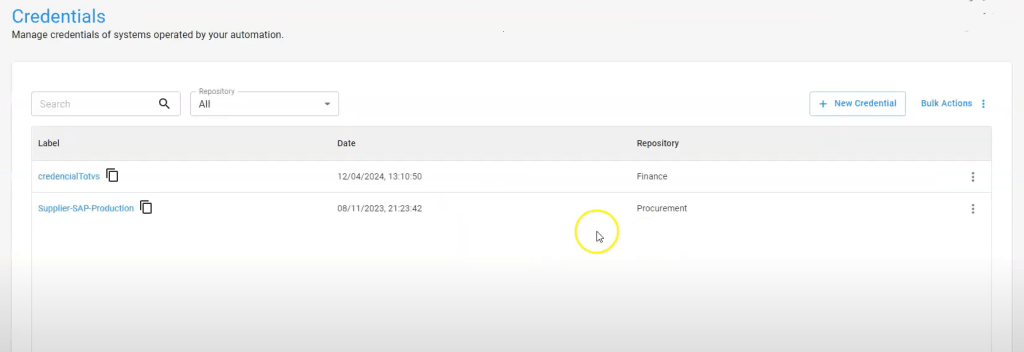
Credential Management in BotCity Orchestrator
In BotCity, developers can create and manage credentials directly through the orchestrator interface.
After creating a new credential, assigning a label, and selecting the appropriate repository, keys are securely stored. An API is available to dynamically access credentials during robot execution. This allows credentials to be updated without disrupting running automations, enhancing security and operational resilience.
5. Audit and Monitoring in Python RPA
Monitoring and auditing actions within RPA platforms is a critical security practice, as RPA operations often handle sensitive data.
For companies working with code-based automation, BotCity enables users to view audit logs within the orchestrator, filter events by user, source, and date, and integrate this data with other BI platforms through BotCity Insights for enhanced observability.

Ready to Enhance the Security of Your Python Automations?
Here are a few key takeaways: the most crucial part of any RPA project is process analysis and mapping out edge cases. Security is a shared responsibility among all people and systems involved at every stage of the process.
Now, you can start implementing security measures to better protect your code, operations, and company. And if your team is looking for an orchestration platform for Python, BotCity is worth exploring.
You can try our orchestrator for free for 30 days or reach out to our team for a demo of our advanced features designed for complex operations.



